
How dental innovation drives practice profitability?
Digital dentistry has greatly improved our oral healthcare as traditional treatments can now be performed effectively and gently, offering more profits to dental investors.
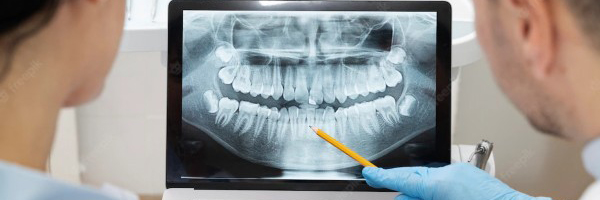
Digital dentistry is a concept that is becoming more and more articulated every day with the latest technological advances registered in this field. Innovative best practices address the challenge of managing a single practice or complex dental tissue. The results (in both sectors) help the dentists or the oral healthcare providers to offer a more superior patient care that sets them apart from their competitors.
You may hear a lot about the "next-gen" technology in dentistry. This can include software or various automation-oriented techniques.
In any case, participating in a workflow and digital dental care revolution will have a significant impact on clinical practice and the standard of care for organizations.
This blog provides an overview of existing digital technologies in dentistry that have also proven useful in pediatric dentistry and orthodontics. Whether it's supporting diagnostics, simplifying pediatric dentist or patient procedures, or creating a friendly environment, digital devices can make a significant contribution to improving the quality of treatment and attract better ROI for dental investors as well as dentists.
Introduction to Digital Dentistry
Technological advances like AI have led medicine to a new era. Today, the dental digital solution is no longer a sci-fi concept, but a complete practical reality that allows patients to receive the latest solutions to traditional dental problems.
Some digital technologies available in dentistry have already been proven in pediatric dentistry. Digital radiography, along with a range of state-of-the-art non-invasive cavities detection tools, assists dentists in diagnosis, computer-controlled delivery of topical anesthetics or nitrous oxide, digital impressions, CAD / CAM restorations, and digital-based.
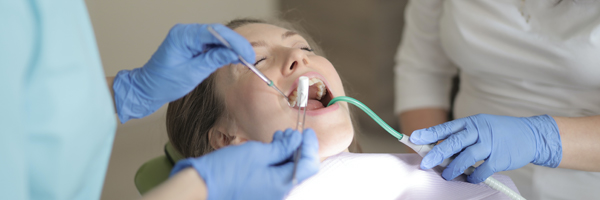
Drilling templates improve treatment options. Digital photography and virtual reality are especially useful for pediatric patient management, as growth monitoring and behavioral management are two of the main concerns of pediatric dentistry.
All of the above technologies incorporate the latest technological advances to help dentists provide patients with superior oral health solutions with improved efficiency, accuracy, and comfort.
According to experts, dental innovation will ultimately improve and expand access to dental care, enable same-day treatment, reduce doctor consultation, and make a healthy smile more affordable.
The more high-quality digital information is available to dentists, the greater the potential for more accurate diagnosis and treatment. For example, data such as age, medical history, dental history, and genome can help a dentist determine susceptibility to different types of oral disorders. Shortly, doctors and dentists will increasingly tailor treatments to your genetics and make decisions that reflect what has proven to be most effective for your genome and specific physiology. Or you may even decide how best to treat you based on the specific bacteria that are causing the problem.
Not all digital opportunities in dental care are widespread, so their benefits are not yet fully understood. The knowledge gained from them for basic research, clinical research, and innovative treatment protocols is not just an industry-oriented test, but patient-centric results to enable a link between the oral cavity and general health.
In summary, Digital dentistry and dental research open up unimaginable opportunities – both from a scientific point of view and Profitability for the investors.
Now, we will go over some of the latest dental innovation trends and they have impacted the direction of dental research and its stakeholders shortly.
Rapid prototyping
RP is a fast and automatic method of using a 3D printer to build a three-dimensional (3D) model of an end product or part of a whole. The additive manufacturing process allows you to cost-effectively produce complex 3D geometry from a variety of materials while minimizing material waste.
Even though the future looks very promising from a technical and clinical standpoint, it is not clear how RP and its products will be regulated. This uncertainty is a problem for manufacturers, healthcare providers, and patients.
In digital dental care, one of the primary concerns is the usage of material. Materials commonly used for RP are currently limited to temporary restoration as only short-term to medium-term oral retention is approved, and final tooth reconstruction is not yet intended. For dental technicians, RP has great prospects, not only for the mass manufacturing of tooth models but also for the manufacturing of implant-going templates.
These indications do not require long-term oral retention. From an economic point of view, the ability to simultaneously carry out mass manufacturing in a reproducible and standardized way is a great advantage. Another important area of the application is the use of 3D printed models in CBCT or CT-based dental education. However, early studies have shown that 3D-printed dental models can show changes in dimensional accuracy over four weeks or more. In this context, further research is necessary to compare different 3D printers and material combinations for clarity.
A fully innovative aspect is the synthesis of biomaterials for the artificial fabrication of missing tooth structures using Rapid Prototyping technology. Instead of using a ready-made tooth database, patient-specific digital tooth records can be captured at the end of growth and used for future tooth reconstruction. Apart from that, the entire tooth can be altered or renewed as a customized dental implant. Rapid prototyping is most likely to provide cost-effective manufacturing and highly customized solutions in different areas of dentistry that can be tailored to the specific needs of each patient.
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality
AR is an interactive technology that enhances the real-world environment with perceptual information from computer animation. Put simply, Augmented Reality extends real life with online content. In most cases, you need to show additional digital information in your live image or video.

Virtual Reality, on the other hand, uses only artificial computer scripts without reference to reality. Depending on the technology, all possible sensitive prints, primarily visual, audio, and tactile, can be used collectively or in any combination.
Today, AR / VR technology applications are growing rapidly across digital dentistry, with many developments that are appealing to patients and healthcare providers.
AR / VR software allows users to overlay patient images with natural movements using virtually created visualizations. Each 3D model, for example, a possible reconstructive prosthetic design, can be extended to individual patient situations to pre-simulate various promising results without invasive work procedures. These digital models can be displayed in real-time, which not only facilitates communication with patients to explain complex treatment procedures in an easy-to-understand manner but also facilitates communication between dentists to make treatment more predictable and efficient.
With the implementation of Digital dentistry, opportunities will continue to expand and routine dental care will become easier. An interesting sign is to extend the CBCT-based virtual implant program directly into the oral cavity or use an intraoral scanner (IOS) to project and view the optically captured area with AR glasses.
Another promising area of interest is the area of dental education. It provides theoretical knowledge and hands-on exercises and provides interactive instruction with 24/7 access and objective assessment.
Dental preparation education based on augmented and virtual reality provides an efficient and autonomous learning experience, especially for dental students. Early research suggests that AR/VR technology stimulates a greater sense of successful learning.
Artificial Intelligence
AI or Artificial Intelligence including Machine Learning and Deep Learning is a more subtle method, such as a virtual assistant called "Siri" or "Alexa", but it's already pervasive in everyday life.
The foundation of AI is the increased ability of computers to think and complete tasks currently being performed by humans faster, more accurately, and with less resource consumption. This makes AI technologies ideal for tasks that require the analysis and evaluation of large volumes of data.
Repetitive tasks are tedious, tedious, and increase the risk of errors for humans in the long run, but AI-powered applications show no signs of fatigue. Unlike humans, artificial learning processes always improve their performance as their workload increases. Moreover, compared to humans who are endowed with innate prejudice, computers are less prejudiced and can prematurely judge things in different ways.
The most valuable indications for using AI and ML in dentistry are all areas of diagnostic imaging in dental maxillofacial radiology. Currently, applications and research for AI purposes in dental radiology are focused on automatic localization of head measurement landmarks, diagnosis of osteoporosis, maxillofacial cysts and/or tumor classification/segmentation, and periodontitis / apical disease identification.
Computer software program that analyzes x-ray reports must be integrated with big datasets to understand significant patterns. The diagnostic performance of the AI model depends on the algorithm used and also on the observer who labels the dataset.
The generalizability and reliability of these models should be verified using appropriate representative images. AI software must be able to read and process new information sent in the right context through images, text, and spoken language.
Finally, the software needs to be able to make intelligent decisions related to this new information, learn from mistakes, and improve decisions for future processing.
A useful AI system needs to do all this at about the same time that humans can perform specific tasks. Until now, large-scale applications of AI have not been technically feasible or cost-effective, so technological advances have been dramatic and many AI models will soon emerge, but the reality of AI is normal.
Personalized Oral Care
With standardized diagnostics and a generally accepted data format, Electronic Health Records (EHR) is an essential door-opener for personalized medicine and predictive models that test a wider population. Structured and systematic collection of patient information is an effective tool in health economics.

Health data can be obtained from a variety of new sources such as routine dental treatments and clinical trials, as well as data on general IoT and especially social determinants of health. Linking individual patient data from different sources enables the diagnosis of rare diseases and a whole new research approach. A large population-based patient cohort study may reveal unrecognized relationships between diseases and create prognostic models for new therapeutic concepts. Linking patient-level information to population-based citizen cohorts and bio-banks provides the necessary reference for diagnostic and screening cutoffs that can identify new biomarkers through individualized health surveys.
EHR has great power to transform research in both directions. On the other hand, digitized transparent patients can be stigmatized and categorized by insurance companies, which causes disabilities not yet recognized by society. Therefore, linked biomedical data that support registry-based research poses some risks and methodological challenges to clinical research. The development of algorithms for statistical calculations, including proper security settings and interpretation of collected health data.
Overall, personalized medicine is the key to opening new horizons in dental research. Genome sequencing, combined with advances in medical imaging and regenerative technologies, has redefined personalized medicine using novel molecular tools to deliver accurate patient care.
By using genomic information to identify individual biomarkers, it has the potential to revolutionize healthcare. This vision is an interdisciplinary approach to analyzing samples of dental patients, allowing dentists, doctors, and nurses to work together to understand the relationships between diseases in a cost-effective manner.
Telemedicine
Tele-healthcare permits a handy manner for patients to foster self-care whilst probably decreasing dental clinic visits and tour time.
Considering the developing range of the aged populace with decreased mobility and/or nursing home-stay, special-care sufferers, in addition to people living in rural areas, those affected person agencies might advantage appreciably from teledentistry. Measures to be taken in case of dental trauma may be successfully communicated with the aid of using dental care apps and maybe regularly used for out-of-workplace hours.
In general, remote dentistry shifts to preventative care rather than expensive treatment, providing easier access to care and a lower-cost option for patients. Patients can also consult with a dentist who is not otherwise available, for example through live video streaming consultation. However, it should be emphasized that remote dentistry cannot replace a real dentist. Rather, it should be understood as an additional tool.
Today, remote dentistry is only an early start-up stage. Early studies focused primarily on certain rare diseases that may require surgery, but remote radiation systems in general dental practice are useful and unnecessary for the differential diagnosis of common lesions. There is evidence to suggest that cost savings can be achieved. There is a fundamental need to regulate the expanding field of telemedicine with guidelines for ensuring clinical quality standards.
Laws need to be clearly defined and specified for the routine implementation of national remote dental platforms. The technical requirements must be met and the security standards for sensitive patient information must be assured by well-defined regulations.
Digital Dentistry is the future of dental care practice
Several advances have made it possible to use a smartphone to perform the first scan at home or in a local clinic. These techniques centralize dental care and enable rapid diagnosis of basic problems in people everywhere, even in remote areas and places with few dentists.
Ultimately, someone living in a developing country can upload their information and get the same initial analysis as a New Yorker visiting a senior dentist on Madison Avenue.
With the advent of dental innovations, basic imaging and other diagnostics do not need to be performed by highly trained professionals. Shortly, technicians will become an integral part of dental practice and dentists will focus on complex and complex procedures that require specialized knowledge. Ultimately, this should reduce costs.
The future of dentistry looks very different from today's practices. No drilling, no injections, easy access, and shorter treatment times. In general, you can reduce cavities and periodontal disease with a greater focus on prevention.
Conclusion
Adopting Digital dental care solutions is essential when it comes to providing quality treatment to patients.
Also, the oral care industry is expanding rapidly. The global dental equipment market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 5.7% between 2014 and 2019, reaching a total of USD 7,138.9 million in 2019. In addition, the idea of oral care is expected to change significantly over the next 10 years. For this reason, dentists need to stay abreast of technological advances in the dental industry.
As competition in this area intensifies and new practices models emerge, the need for efficiency becomes paramount. Professionals need to provide optimal dental care while maintaining the profitability and growth of their practice. Despite the rapid growth of the industry, dentists can invest in technology that can withstand the challenges of time to maximize patient comfort and create the right environment for growing practice. Investing in the right dental technology is the only way to achieve this.